An Audience is defined by a very specific combination of visitors’ characteristics and their actions within the website. It is defined by a set of rules, and relations between those rules, that can be precisely arranged in very descriptive and complex formulas. What makes the Audience Definition so powerful and truly sets it on a league of its own is the ability to specify when and in what order those rules occur. Once e-Marketer Recognizes that a visitor is a member of a defined Audience Group (all the combined rules where matched), linked Content Adjustments are executed, and the visitor is presented with personalized content in real-time. Below is a complete, step by step tutorial teaching you how to define Audience Groups, and present them with highly Tested and Optimized Personalization Actions.
Audience Definition Examples
- Visitors browsing the website from the UK.
- Visitors interested in renting a GPS + with maps of Greece + with a large screen.
- Visitors interested in a certain product + who have completed an order in the past.
- Visitors that were referred from a Google sponsored link + searching for televisions OR projectors.
Rules, Events and Sequence
Rules are the building blocks of an Audience Definition; they are the conditions that have to be met by a visitor in order to belong to the Audience. Rules can be interrelated with logical operations, creating a more complex Rule. Each Rule is a mathematical relation; therefore, it is comprised of a relational operator, a Metric on one side, and a Value, or a combination of several values and logical operators, on the other. ▪ Country = UK ▪ Total Time on Site > 5 minutes ▪ Referrer = Google OR Yahoo ▪ Keyword = GPS + Greece ▪ Operating System = NOT Windows
Defining an Audience
- In the Audience section click on ADD RULE .
- Notice how the menu cascades downwards, exposing the rule itself( top of the box) and often the customization options( in the middle of the box).
- To change to a different Audience Rule, simply click on the rules category on the left side, choose a metric from the cascading menus. Each Rule is defined by one metric.The cascading menu shows a tool-tip with a brief description for each metric. After choosing a metric, the chosen metric’s settings dialogue offers more information in a pop-up that you can see by hovering with your mouse over the question mark icon located next to the metric’s name.
- You can rename each rule to a more descriptive name, by clicking on the on the name of the rule in the orange rectangle.
- To add a rule, hover over an existing rule’s name or over a left bracket and click the plus sign.
▪ Click the operator to switch between AND, OR and XOR.
- To add brackets, hover over an existing rule’s name and click the left bracket sign; to close the bracket hover over the rule’s name to whose right you want the closing bracket and click the right bracket sign.
- Hover over an existing rule’s name or over a left bracket and click on the ‘NOT’ operator to negate the whole preposition. The ‘NOT’ operator is black when it is active and light gray when it is inactive.
- To remove a rule or a bracket, hover over them and click the minus sign.
Advanced Audience Settings:
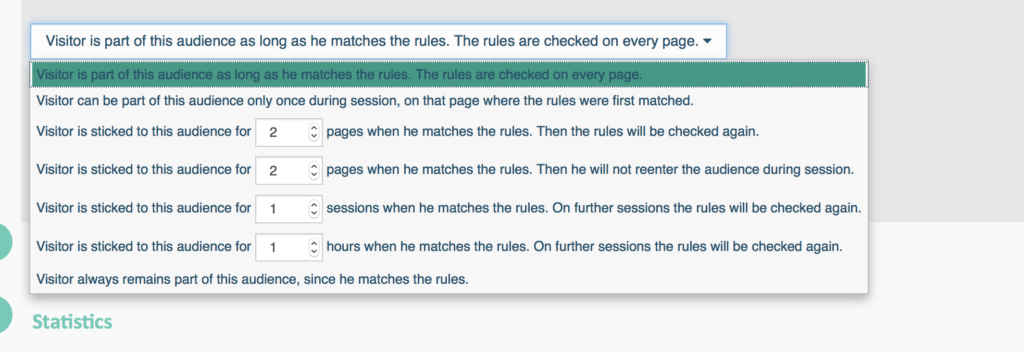
Keeping the Visitor as a Member of the Audience.
e-Marketer checks for a match between a visitor and an Audience each time that a record is added to the database (usually a page view). Sometimes, you may want to keep the visitor in an Audience for longer than one session, or not allow him to match the audience again. To define the conditions controlling the visitor matching an audience, simply choose the most appropriate conditions below the Audience Rules. For Example: ▪ A visitor has matched the ‘Completed an order on-line’ Audience; you want the Audienceto ‘stick’ forever because there is no need to show him the ‘How to order on-line’ banner. ▪ A visitor matched a Audience and triggered the display of a ‘Free delivery’ offer; you choose not to show the same offer during the next five pages. You can specify for how many pages or sessions the Audience will be ‘sticked’. You can also specify if the Audience can be matched again or if it can only be matched once.
Audience Groups
Audience groups allow you to define several audiences of which only one can be matched at a time. This could be useful when a visitor is matching more than one Audience and you need to manage conflicts. For example: When a visitor arrives to the website after searching for “family vacations in Italy” you’ll want to keep the visitor in that Audience in order to offer a personalized experience even in future visits. If, afterwards, the same visitor arrives to the website after searching for “romantic caribbean cruise”, you’ll want the visitor to match only the more recent search terms. Visitors that match the conditions of more than one Audience of the same group will be considered as matching only one of those segments, based on the configuration of the following three parameters: ▪ Audience Group Priority (importance): a numeric value that is assigned to the Audience Group. It indicates the Audience group’s priority over other segment groups. A lower number defines a higher Audience group priority. (The value “1” indicates a segment group with the highest priority). To define a Audience Group Priority to your segment group, simply add a numeric value next to it and save your segment. ▪ Group condition: First decision: can have any one of the following attributes: Last, First, Importance ▪ Group condition: Second decision: can have any one of the following attributes: Last, First, Importance Examples: If you define the audience group with the following configuration: First decision: Importance ; Second decision: Last, it means that if several audiences are matched, e-Marketer is instructed to search for the audience with the highest priority (lowest numeric value) and only activate it. In case all audiences have the same priority, the second decision is checked and the last audience to execute is the one that will be activated. Another example: First decision: Last; Second decision: Importance, it means that e-Marketer is instructed to first search for the audience that happened last and only activate it. In case all audiences didn’t happen yet or all happened at the same time, the second decision is checked and the audience with the highest priority (lowest numeric value) is activated.
Goals
Goals let you cumulatively measure the efficiency of your website; they are a fundamental component for the success of any organisation.
It may be obvious what are the main Objectives of the website; most of the times it will be generating profit in one way or another. On the other hand, it is not always obvious what Goals must be achieved to accomplish those Objectives. Here is an example: ▪ Visitor A completed an online order in your website. ▪ Visitor B just viewed two pages for a total of 40 seconds. ▪ Visitor C viewed ten pages for a total of five minutes, then visited a page in your website regarding payment options and then downloaded the map to your physical store and printed a coupon. The first case clearly represents an accomplished objective. On the other hand, though there are no completed orders in neither of the two other cases, visitor C is a lot closer to conversion than visitor B; downloading the map and printing a coupon are significant. A Goal can be anything of worth for your business, such as downloading a map, printing a coupon, filling a form, solving a problem through the support pages; anything that creates profit, increases the likeliness of generating profit or increases engagement. The Goal Value for the Audience lets you establish how much is the combination of attributes and actions performed by a visitor worth for the website. At the bottom of the expanded “Audience Advanced Settings” can set a fixed numerical Goal Value or extract it from a specified Container (for example, cart value).
Reference: types of Dimensions and Metrics
Came From How did the visitor reach the page
- Keywords by typing specific keywords in a search
- Direct by typing a URL in the browser
- Referring sites from specific referring sites
- Search engines from specific search engines
- Internal search keywords searched in the site (to define an internal search go to Settings)
- Internal page by clicking a link in a page within the site
Visitor’s properties Information about the visitor’s location and specific to his visit
- IP IP address
- City City in which the IP address is located
- Country Country in which the IP address is located
- Region Region in which the IP address is located
- Continent Continent in which the IP address is located
- User id Unique User ID as defined by e-Marketer
- Visit type New or returning visitor
- Session count How many sessions since the cookie was created
- Time since last visit Time since the last page view in the previous session
- Language Browser language preference
- Company Company to which the IP address is assigned
Pages visited in the site Filter by specific pages or groups of pages
- All pages Any page
- Belongs to group Pages that belong to a defined Page Group
- URL parameters Specific parameters in the URL and their values
- URL path Full path in the URL
- Host name Host name in the URL
- URL fragment The part of the URL to the right of the first # symbol
- Full URL The whole URL
- Page Title The page title, as defined between the
Actions/Containers/Audience Events that happened
- Containers found Value and quantity of Containers in the site
- Actions executed Actions executed in the site
- Segments (Audiences) matched Segments matched in the site
Visitor’s system info Technical information on the visitor’s OS and browser
- OS name and version that the visitor is using in this visit
- Browser name and version that the visitor is using in this visit
- Screen Resolution Display resolution as set in the OS
- Screen bit depth Display bit depth as set in the OS
- Platform Browsing device’s hardware type
- Rich media plug-ins Multimedia plug-ins’ versions
- Browser settings Checks if cookies, Ajax and Java are enabled
- Mobile browsing Checks if browsing through a mobile device
Visitor’s behaviour Actions performed by the visitor, and measurement of activities
- Site enter time Time of the first page view in this session
- Page enter time Moment that the current page has been loaded
- Average time on page Total time on pages / Total pages viewed
- Total time in focus Total time that pages were in focus (i.e., active)
- Page events Count of page events (scrolling, key presses, and mouse clicks)
- Page views Count of page views
- Total time on pages Total time on pages
- % of time in focus Total time in focus / Total time in site, in this session
- % of pages that lost focus Times that pages lost focus / Total pages viewed, in this session
- SSL connection Checks if connection is HTTP or HTTPS
- Page refresh Times that a page refresh was performed
- Links Name and type of hyperlinks clicked
Goals achieved Goals achievement
- Quantity of goals Quantity of achieved goals
- Value of goals Total value of the achieved goals
Delivering Targeted Content
After you are done defining your Audience, you can now set up all Personalized Content Adjustments that members of that audience will be exposed to.
- Go to the “Targeted Content” section at bottom of the page.
- Click on the green “+ Targeted Content” button.
- To create a new Personalized Content adjustment, choose the appropriate widget from the List.
Comprehensive Personalization Content Adjustments Guide
- WYSIWYG – the WYSIWYG editor allows you to create changes in the site/page content for testing or personalization activities in real-time directly from your existing site pages.
- HTML – Inserts HTML into a page, using the HTML editor below.
- HTML Loader – Dynamically extracts content from a web page and inserts it into an area of the current page.
- Image – Inserts an image into a page, by providing the image’s URL or by uploading it using e-Marketer’s Media Manager.
- JavaScript – Executes custom JavaScript in a page, by providing the JavaScript code in the box below. It will be executed every time the page loads.
- Redirect – Performs a page redirection, by specifying the target URL, whenever a visitor reaches any of the pages specified in the action.
- Popup – Shows a popup whenever a visitor reaches a specific page, by specifying the target URL.
- Form – Allows you to create powerful custom forms and use the collected data for segmentation and analytics.
- Font Properties – Changes any font property within the text displayed.
- Replace text – Finds and replaces text strings within the page’s displayed text, as well as in the URLs of links to pages, images, and background images.
- Replace image – Finds and replace images within the page’s layout or the background image.
- Replace number– Finds and replace numbers within the page and change them by applying operations.
- CSS Style – Applies specified CSS attributes to elements.
- Email – Sends a customised email every time that a segment linked to the action is matched.
- Newsletter – Add or remove users from one mailing list to another base on their site activity.
- WordPress Theme – Changes your WordPress theme per segment.
- WordPress Post – Change the post of a page in your WordPress website, per segment.
- Facebook Connect – Displays the ‘Facebook Connect’ button to allow visitors to connect to your website using their Facebook account and share their information with you.
- Facebook Share – Displays the ‘Facebook Share’ button.
- Facebook Publish – Post a message to your visitors’ Facebook wall.
- Facebook Publish (server side) – For visitors that have authorized your website (with “Facebook Connect), does not require asking for permission when posting.
- Facebook Like – Displays the ‘Facebook Like’ button.
- Google Analytics – Transmit advanced segments and events to your Google Analytics account.
- Google AdWords – Transmit complex goals that include advanced conditions, events and dynamic content to your Google AdWords account.
- Google Remarketing – Use Remarketing to show ads to your visitors after they leave your website.
- Google DoubleClick – Transmit information about your visitors to your DoubleClick account to show highly relevant ads.
- Dynamic parameter : e-Marketer HTML Editor is used in Content Adjustments such as HTML and Pop-up and makes use of Dynamic parameters